Welcome to the “Ultimate Guide to Solar Panels 2024,” your definitive resource for everything you need to know about solar panel technology. Here, we’re dedicated to bringing you the most up-to-date and comprehensive information available. In this guide, we delve into every aspect of solar panels, from the various types available and their efficiency, to a detailed cost analysis, the installation process, and much more.
Whether you’re in the UK and curious about government incentives and subsidies, concerned about the environmental impact, or interested in the nuts and bolts of maintenance, durability, and energy output, we have you covered. We also explore how solar panels integrate into different settings, considering location and climate factors, and debunk common myths and misconceptions.
By the end of this guide, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge to make informed decisions, with our conclusions and recommendations guiding you every step of the way. Join us as we illuminate the world of solar panels in 2024, paving your path to a more sustainable future.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Solar Panels
- Types of Solar Panels
- Efficiency of Solar Panels
- Cost Analysis
- Installation Process
- Maintenance and Durability of Solar Panels
- Energy Output
- Government Incentives and Subsidies
- Environmental Impact
- Compatibility and Integration
- Location and Climate Considerations
- Common Myths and Misconceptions
- Conclusion and Recommendations
Introduction to Solar Panels
What are Solar Panels?
Solar panels, at their core, are devices that convert sunlight into electricity. They are composed of numerous solar cells made from materials like silicon, which is known for its photovoltaic properties. When sunlight hits these cells, it triggers an electrical process that generates current.
Why Solar Panels?
The shift towards solar energy is driven by a growing recognition of its numerous benefits. Solar panels offer a clean, renewable source of energy, significantly reducing dependence on fossil fuels and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. In an era of increasing environmental awareness, solar panels stand out as a sustainable solution to our energy needs.
The Evolution of Solar Technology
From their humble beginnings in the mid-20th century to the highly efficient models available today, solar panels have undergone significant technological advancements. The evolution of solar technology has made it more accessible and affordable for a wide range of applications, from small-scale residential setups to large-scale industrial installations.

Types of Solar Panels
When exploring the world of solar energy, understanding the different types of solar panels is essential. In this guide to solar panels, we’ll start with a table overview of the most common types available on the market, before delving into the details to help you make an informed decision for your specific needs.
Summary of Solar Panel Types
| Type | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages | Ideal Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monocrystalline | Single-crystal silicon | Efficiency >22% | High cost (£4,000-£12,000) | Residential, ample sunlight |
| Polycrystalline | Multiple silicon crystals | Efficiency 13-16% | Requires more roof space | Budget-conscious, ample space |
| Thin Film | Multiple photovoltaic films | Efficiency 7-13% | Larger installations needed | Unconventional roofs, RVs |
| Transparent | For glass surfaces | Efficiency 1-10% | High cost, low savings | Commercial, natural lighting |
| CPV | Curved mirrors to concentrate | Efficiency 35-50% | Not for residential, limited regions | Large-scale, high solar irradiance |
| PERC | Technological enhancement | Improves efficiency | Less efficient than newer tech | Moderate efficiency boost |
| Solar Tile | Regular roof tile appearance | Aesthetically integrates | Efficiency 10-20%, higher cost | Properties with strict regulations |
| Solar Thermal | Heats water using sunlight | Reduces heating bills by up to 50% | Only for water heating | Domestic hot water, cost-effective |
- Monocrystalline
- Description:
- Monocrystalline panels are crafted from single-crystal silicon, processed into bars, sliced into wafers, and coated with anti-reflective material, resulting in a sleek, dark appearance.
- Advantages:
- Highest efficiency among commercially available panels, typically exceeding 22%.
- Aesthetically pleasing black panels enhance the visual appeal of rooftops.
- Significant reduction in electricity bills, averaging a 64% decrease.
- Long lifespan ranging from 25 to 40 years, ensuring durable performance.
- Break-even point of 14 years, making them a worthwhile investment over time.
- Disadvantages:
- Higher upfront cost compared to other panel options.
- Initial investment typically ranges between £4,000 and £12,000.
- Limited availability in terms of design options due to their distinctive appearance.
- Ideal Use:
- Ideal for residential households seeking maximum energy efficiency and long-term savings.
- Suitable for homeowners willing to invest upfront for significant long-term benefits.
- Recommended for locations with ample sunlight exposure to optimize energy generation.
- Description:
- Polycrystalline
- Description:
- Polycrystalline solar panels are manufactured by melting multiple silicon crystals and pouring them into a square mould, resulting in a distinctive blue mosaic appearance.
- Advantages:
- Slightly more eco-friendly manufacturing process, with less silicon wastage compared to monocrystalline panels.
- Generally the more economical option in terms of upfront cost.
- Disadvantages:
- Higher cost per watt compared to monocrystalline panels.
- Lower efficiency ratings, typically ranging from 13% to 16%, requiring more roof space for equivalent power output.
- Appearance is less sleek and modern than monocrystalline panels.
- Ideal Use:
- Suitable for budget-conscious homeowners seeking solar energy solutions at a lower upfront cost.
- Recommended for locations with ample roof space to accommodate larger panels for desired power output.
- Ideal for those prioritizing cost-effectiveness over maximum energy efficiency and aesthetics.
- Description:
- Thin Film
- Description:
- Thin film solar panels are constructed by layering multiple thin films of photovoltaic material, such as amorphous silicon, cadmium telluride, copper indium gallium selenide, or organic PV cells.
- Advantages:
- High flexibility allows installation on non-flat surfaces and wrapping around objects.
- Ideal for homes with limited roof space or mobile structures like RVs and sheds.
- Generally more affordable than traditional crystalline solar panels.
- Disadvantages:
- Lower efficiency ratings compared to other solar panel types, typically ranging from 7% to 13%.
- Limited power output due to lower efficiency, requiring larger installations to achieve desired energy production.
- Ideal Use:
- Perfect for residences with unconventional roof shapes or limited roof space, enabling flexible installation options.
- Recommended for mobile homes, sheds, and recreational vehicles seeking solar energy solutions.
- Suitable for budget-conscious consumers prioritizing affordability over maximum energy efficiency.
- Description:
- Transparent
- Description:
- Transparent solar panels are designed to be placed on glass surfaces, allowing sunlight to pass through while generating solar energy. They hold the potential to be integrated into various applications, including windows, mobile devices, and greenhouses.
- Advantages:
- Allows sunlight to pass through, maintaining visibility and natural lighting indoors.
- Versatile application on multiple surfaces, including windows and glass facades.
- Aesthetic appeal with no significant visual drawbacks when installed on buildings.
- Disadvantages:
- Low efficiency rating, typically ranging from 1% to 10%, resulting in limited energy generation.
- High upfront cost, making them less economically viable for residential applications.
- Limited cost savings compared to traditional solar panels, often making them more suitable for commercial use.
- Ideal Use:
- Ideal for commercial buildings seeking to incorporate solar energy generation into their architecture without sacrificing aesthetics.
- Suitable for applications where maintaining visibility and natural lighting is essential, such as office buildings, retail spaces, and greenhouses.
- Recommended for future-oriented projects exploring innovative ways to harness solar energy while maintaining functionality and aesthetics.
- Description:
- Concentrator Photovoltaics (CPV)
- Description:
- Concentrator Photovoltaics (CPV) utilizes curved mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto small, highly efficient solar cells, achieving intensities of 1,000 suns or higher.
- Advantages:
- Exceptionally high efficiency rating, ranging from 35% to 50%, maximizing energy generation potential.
- Utilizes sunlight intensities equivalent to 1,000 suns or more, significantly enhancing energy output.
- Capable of generating solar energy even in low-light conditions due to concentrated sunlight.
- Disadvantages:
- Not readily available for residential use, primarily utilized by energy companies for large-scale installations.
- High upfront cost and complexity make CPV systems prohibitively expensive for individual homeowners.
- Limited geographical applicability, typically found in hot regions with abundant sunlight, such as Spain, South Africa, and the US.
- Ideal Use:
- Ideal for large-scale solar energy projects owned by energy companies, particularly in regions with high solar irradiance.
- Suitable for installations requiring maximum efficiency and energy output, such as utility-scale solar farms and solar power plants.
- Recommended for areas with consistent sunlight and high electricity demand, where CPV systems can maximize returns on investment for energy companies.
- Description:
- Passivated Emitter and Rear Contact (PERC)
- Description:
- Passivated Emitter and Rear Contact (PERC) is a technological enhancement incorporated into domestic solar panels during the manufacturing process to improve efficiency.
- Advantages:
- Enhances panel efficiency by making the rear side reflective, allowing for better absorption of unabsorbed light.
- Passivation layer reduces heat absorption, minimizing efficiency losses in high-temperature environments.
- Offers a cost-effective option for households seeking improved solar panel performance without investing in top-tier models.
- Disadvantages:
- Less efficient compared to newer technologies like Tunnel Oxide Passivated Contact (TOPCon) or Heterojunction (HJT).
- Decreasing popularity among leading manufacturers in favour of more advanced panel designs.
- Limited efficiency gains compared to top-tier panels, making them less attractive for installations prioritizing maximum energy output.
- Ideal Use:
- Ideal for homeowners seeking a modest efficiency boost for their solar panels without significant investment.
- Suitable for regions with high ambient temperatures where minimizing efficiency losses due to heat is crucial.
- Recommended for budget-conscious consumers looking for a cost-effective solution to improve their existing solar panel systems.
- Description:
- Solar Thermal
- Description:
- Solar thermal panels, also known as solar water heaters, utilize the sun’s rays to heat domestic hot water, offering an energy-efficient alternative to traditional heating methods.
- Advantages:
- Significantly reduces heating bills by up to 50%, providing substantial savings on household energy expenses.
- Comprised of either flat plate panels or evacuated tube collectors, efficiently capturing solar warmth to heat water within the system.
- Easy installation and compatibility with existing boilers and immersion heaters, requiring minimal additional infrastructure.
- Disadvantages:
- Primarily provides hot water for domestic use and does not generate electricity, limiting its utility to heating applications only.
- Unable to supply 100% of hot water demand, necessitating supplementary heating methods during periods of high demand or low sunlight.
- Reliant on sunlight availability, with reduced efficiency during cloudy or overcast conditions, potentially impacting hot water production.
- Ideal Use:
- Ideal for homeowners seeking a cost-effective and environmentally friendly solution for heating domestic hot water.
- Suitable for residential properties looking to reduce reliance on conventional heating methods and lower overall energy consumption.
- Recommended as part of an integrated heating system, complementing existing boilers or immersion heaters to maximize energy efficiency and cost savings.
- Description:

In conclusion, when considering a solar panel installation, it’s crucial to weigh the pros and cons of each type. Your choice will depend on factors like budget, available space, aesthetic preferences, and energy needs. This guide to solar panels aims to provide a clear understanding of your options, making your journey towards sustainable energy a well-informed one.
Efficiency of Solar Panels
Understanding the efficiency of solar panels is key to maximizing the benefits of solar technology. In our comprehensive “Guide to Solar Panels,” we delve into what makes a solar energy system effective and the factors that impact its performance.
Key Factors Influencing Solar Panel Efficiency
Efficiency begins with the type of solar panel. Monocrystalline and polycrystalline silicon panels are prevalent, with monocrystalline panels generally offering higher efficiency at a higher cost, while polycrystalline panels are more affordable but less efficient.
Temperature is another crucial factor. Interestingly, solar panels perform better in cooler conditions. Thus, the climate of your location is a significant consideration for installation.
Moreover, the efficiency of solar panels is highly influenced by their placement and orientation. Optimal positioning ensures maximum sunlight exposure. For instance, in the Northern Hemisphere, panels ideally face south.
Additionally, the angle of installation plays a pivotal role. A tilt matching your latitude is often recommended, but householders are usually limited by their existing roof layouts. In such cases, using two different pitches, such as one at 90 degrees, can be an effective strategy. Panels can also be mounted on a tracking (i.e. steerable) structure to adapt to the most efficient angle.
The Impact of External Factors
Beyond the panels themselves, external elements like the shape of your roof, nearby trees, and surrounding buildings can impact efficiency. A roof facing the right direction without shading from trees or other structures is ideal. Interestingly, in lower latitudes, the lower height of the sun usually offsets the efficiency gain from colder temperatures.
Measuring Efficiency
Solar panel efficiency is measured as a percentage, typically ranging from 15% to 22% in 2024. High-efficiency models can exceed 22%, indicating the proportion of solar energy converted into electrical power.
Why Efficiency Matters
High-efficiency panels produce more electricity in less space, a boon for urban homes or limited roof areas. Thus, understanding panel efficiency is not just a technicality but a practical consideration for optimal energy production.
Technological Advances and Future Trends
The solar industry is continually evolving. Technologies like PERC (Passive Emitter and Rear Cell) are pushing efficiency boundaries, shaping the future of solar energy.
In conclusion, comprehending solar panel efficiency is a vital factor to understanding in selecting the right solar solution. Our “Guide to Solar Panels” aims to provide you with the knowledge needed for a sustainable, informed solar energy decision.

Cost Analysis
In this guide to solar panels, we’ll delve into the cost analysis, offering an easy-to-grasp understanding of the financial side of solar panel installation and operation. Our focus will be on the initial investment, government aids, long-term benefits, maintenance costs, and the all-important break-even point.
Initial Investment and Investment Costs
Starting your journey into solar panel adoption involves considering the initial setup costs, including installation expenses. This encompasses not only the price of the solar panels themselves but also additional components such as inverters, mounts, and wiring. The overall cost varies depending on factors like the type and quality of panels chosen, the size of the system required to meet your energy needs, and the complexity of installation.
On average, homeowners can expect to invest between £5,000 to £12,000 for a typical residential solar panel system, before factoring in any potential government assistance or incentives. However, it’s essential to consider additional installation costs, such as hooking up the system to the grid (unless a battery storage solution is utilized), as well as hiring an electrician for professional installation services. These supplementary expenses play a crucial role in determining the total upfront investment required for installing solar panels on your property.
Government Incentives and Subsidies
Thankfully, various government incentives and subsidies can lighten this financial burden. These benefits could take the form of tax credits, rebates, or grants, varying based on your location and current policies.

Long-Term Savings
Here’s where it gets exciting. The long-term savings from solar panels are substantial. Post-installation, they can slash or even nullify your electricity bills. The savings magnitude depends factors such as your energy consumption and your system’s energy output. Moreover, solar panels can boost your property value and last 25-30 years, securing your savings for years to come.
Maintenance Costs
Perhaps contrary to popular belief, solar panels demand minimal maintenance. This typically involves occasional cleaning and infrequent repairs. Plus, most systems come with warranties covering significant issues for about 20-25 years.
Break-Even Point
Crucial to your decision is the break-even point – when your savings equal the initial outlay. This moment usually arrives within 7 to 15 years, influenced by several factors already discussed. To calculate the savings that you could realistically be making, use a free online payback calculator such as this one.

In essence, while the upfront cost of solar panels may seem steep, the benefits of long-term savings, enticing government incentives, and minimal maintenance expenses present a compelling financial case. This guide to solar panels aims to arm you with all the necessary information, ensuring you can make a well-informed choice about embracing solar energy.
Installation Process
Installing solar panels is a crucial step in harnessing solar energy for your home or business. This guide to solar panels will walk you through the installation process, ensuring you have a clear understanding of what to expect.
1. Site Assessment and Planning
Before any actual installation begins, a professional assessment of your site is necessary. This involves determining the best location for your solar panels, considering factors like roof condition, orientation, shading, and local climate.

2. Choosing the Right Type of Solar Panels
In addition to choosing the right type of solar panels, it’s crucial to consider the mounting options available for your installation. There are two primary mounting methods to consider: above existing roof tiles or set within the roof tiles.
- Above Existing Roof Tiles: This mounting option involves installing the solar panels on top of your existing roof tiles. It’s a popular choice for homeowners looking to retrofit their homes with solar panels without the need for significant roof modifications. However, it’s essential to ensure that the mounting system is securely attached to the roof to withstand wind and weather conditions.
- Set Within Roof Tiles: Another innovative option is to integrate solar panels directly into the roof tiles themselves. This method offers a seamless and aesthetically pleasing solution, as the solar panels blend seamlessly with the roofline. Additionally, this approach provides added durability and weather resistance compared to traditional panel mounting systems.
Alternatively, Tesla’s Solar Roof tiles offer a revolutionary approach to solar panel integration by replacing traditional roofing materials with solar-integrated tiles. These durable tiles are designed to withstand all weather conditions while generating clean energy for your home. With the added benefit of Tesla’s Powerwall battery system, homeowners can store excess energy for use during periods of low sunlight or power outages.
When selecting the mounting option for your solar panel system, consider factors such as aesthetics, durability, and compatibility with your existing roof structure. Consulting with a professional solar installer can help you determine the best mounting solution based on your specific needs and preferences.
3. Obtaining Permits
Solar panel installation often requires permits from local government authorities. These permits ensure that your installation complies with local building codes and safety standards.
4. Installation
The installation process involves several key steps:
a. Mounting the Supports: This is the first physical step where mounts are fixed to your roof to support the panels.
b. Installing the Solar Panels: Panels are then securely attached to the mounts.
c. Wiring the Panels: Wiring the solar panels involves connecting them to your power system, a task typically handled by a qualified electrician. This step ensures compliance with electrical safety standards and involves the installation of inverters, which are essential for converting the generated direct current (DC) into usable alternating current (AC) electricity. Inverters can be costly, so selecting the appropriate type and size is crucial.
d. Connecting to the Grid: If your system is grid-tied, it will be connected to the local power grid. For these systems, a grid-tied controller is necessary to manage electricity flow between the panels, the grid, and your home’s electrical system. Entrusting this task to a professional ensures the safe and efficient installation of your solar energy system.
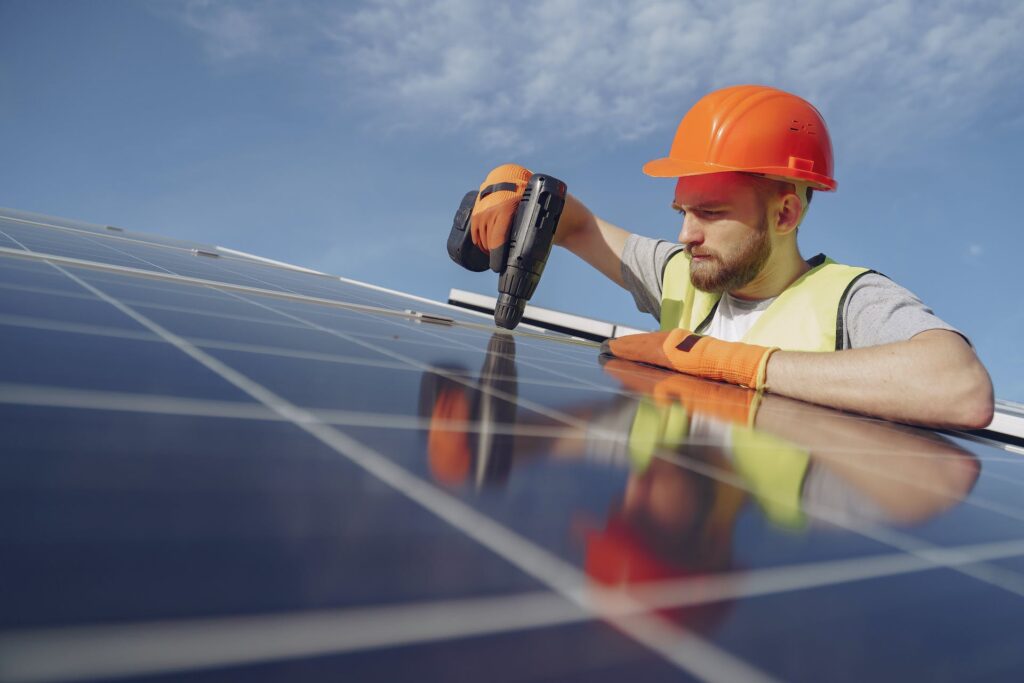

5. Monitoring and Activation
After installation, your solar panel system is connected to a monitoring system to track its performance. Once activated, you’ll begin generating your own electricity, with the potential for significant savings. This is particularly true in the case of grid-tied systems, where excess energy can be sold back to the grid when not needed.

This segment on the installation process in our guide to solar panels is designed to give you a clear and concise overview of what to expect. Each step is crucial for a successful and efficient solar panel system. For more detailed information on other aspects of solar panels, refer to the respective sections in this comprehensive guide.
Maintenance and Durability of Solar Panels
When considering the adoption of solar energy, understanding the maintenance and durability of solar panels is crucial. This section of our comprehensive guide to solar panels delves into these aspects, ensuring you have all the necessary information to make an informed decision.
Minimal Maintenance Requirements
Solar panels are renowned for their low maintenance needs. Once installed, they require minimal upkeep to ensure their efficiency and longevity. This is partly due to the lack of moving parts, which reduces the risk of wear and tear.
Regular Cleaning: The most common maintenance task is cleaning. Panels can accumulate dust, leaves, or snow, slightly reducing their efficiency. It’s generally recommended to clean your solar panels a couple of times a year. However, in areas with more dust or pollen, more frequent cleaning might be necessary.

Durability and Lifespan
Solar panels are designed to withstand various environmental conditions, from scorching heat to heavy snow. Most manufacturers guarantee their panels for 25 to 30 years, but it’s not uncommon for panels to last beyond that.
Degradation Rate: A key term related to solar panel durability is the ‘degradation rate.’ This refers to the rate at which solar panels lose efficiency over time. On average, solar panels degrade at a rate of about 0.5% per year, meaning even after 25 years, your panels could be operating at about 87.5% of their original capacity.
Monitoring for Efficiency
To ensure your solar panels are operating optimally, it’s wise to monitor their performance. Many systems come with monitoring software that allows you to track the energy output. This can alert you to any issues, such as a sudden drop in efficiency, which could be due to physical damage or a need for cleaning.
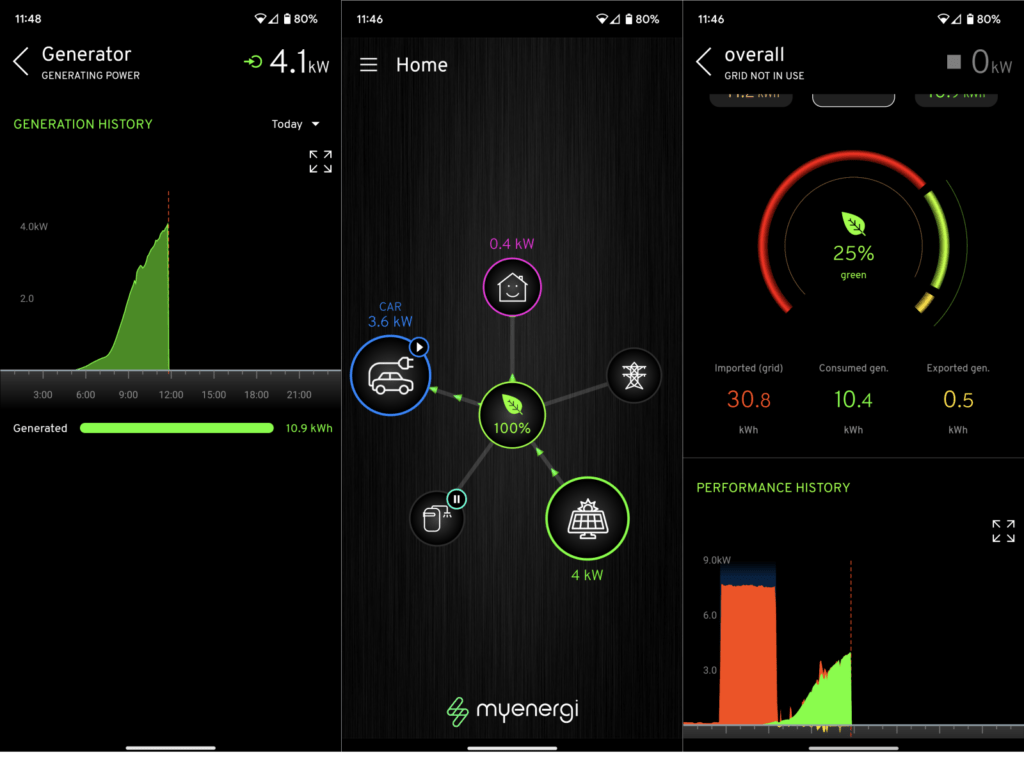
Physical Durability
Solar panels are built to be tough. Most can withstand heavy weather conditions like hail, wind, and snow. The panels’ frames and glass are designed for durability, but it’s always a good idea to check with your supplier about specific resilience features, especially if you live in an area with extreme weather conditions.
Warranty and Insurance
When purchasing solar panels, it’s important to look at the warranty. Most manufacturers offer a 25-year warranty, but terms can vary. Additionally, check with your home insurance provider to understand how solar panels are covered under your policy.

Conclusion
In summary, solar panels offer impressive durability and require minimal maintenance, making them a practical and reliable source of renewable energy. Regular monitoring and cleaning can help maintain their efficiency and prolong their lifespan, ensuring you get the most out of your investment in solar technology.
By understanding the maintenance and durability of solar panels, as highlighted in this guide to solar panels, you can confidently invest in this sustainable energy solution with peace of mind.
Energy Output
Understanding the energy output of solar panels is crucial when considering their installation for your home or business. This section of our guide to solar panels dives into what you can expect in terms of power generation from your solar setup.
How Much Energy Do Solar Panels Produce?
The energy output of a solar panel system varies based on several factors, including the size of the system, geographical location, and the specific type of solar panel used. Generally, a standard residential solar panel ranges from 250 to 400 watts per panel. To put this into perspective, a 5kW (kilowatt) system, which is common in residential settings, can generate about 20 kWh (kilowatt-hours) on a sunny day.

Factors Affecting Solar Panel Energy Output
Several elements impact the energy output of your solar panels. These include:
- Sunlight Exposure: The amount of direct sunlight your panels receive is the most significant factor. More sunlight means more energy production.
- Panel Angle and Positioning: Properly angling your panels to capture maximum sunlight increases efficiency.
- Temperature: Surprisingly, solar panels work best in cooler conditions. High temperatures can reduce output slightly.
- Shade: Obstructions like trees or buildings can significantly decrease energy production.
Maximising Your Solar Panels’ Energy Output
To get the most out of your solar panels, consider the following tips:
- Regular Maintenance: Keep your panels clean and free of debris to ensure maximum light absorption.
- Professional Installation: Ensure your system is installed at the optimal angle and position.
- Monitoring Systems: Use monitoring technology to track energy production and make adjustments as necessary.
This guide to solar panels aims to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of what to expect in terms of energy output. With the right setup and maintenance, solar panels can be a highly efficient source of renewable energy.

Government Incentives and Subsidies
Understanding the UK Government’s incentives and subsidies is crucial for anyone considering the installation of solar panels. This guide to solar panels highlights the key schemes and financial supports available, helping you make an informed decision.
Energy Company Obligation 4 (ECO4) inc LA Flex
The Energy Company Obligation 4 (ECO4) with LA Flex, active from April 2022 to March 2026, is a UK solar grant program available for homes in England, Scotland, or Wales. The eligibility for this incentive is determined by local authorities, offering significant potential savings as households may receive free solar panels, enabling them to reduce their energy bills and carbon footprint.
Solar Together
Solar Together is an ongoing solar grant program supporting homeowners and renters in designated council areas of the UK. Participants in the program can enjoy varied savings, with historical records indicating reductions between 10–25% on energy costs. This community-driven initiative leverages group buying to make solar panel installation more affordable.
Home Upgrade Scheme (HUG2)
Running from April 2023 to March 2025, the Home Upgrade Scheme (HUG2) targets low-income households, particularly those off-grid and living in properties with low energy efficiency ratings in the UK. Eligible households can expect substantial financial support, with the potential to receive up to £10,000 from local authorities to improve their homes’ energy performance.
Home Energy Scotland Grant and Loan Schemes
The Home Energy Scotland Grant and Loan Schemes is an ongoing initiative offering all Scottish households the chance to obtain up to £6,000. This financial assistance aims to support the adoption of solar technology and other renewable energy solutions, facilitating a greener and more cost-effective home environment.
Welsh Government Warm Homes Nest Scheme
The Welsh Government Warm Homes Nest Scheme is a continuous program dedicated to Welsh households receiving income-related benefits and occupying properties with low energy performance ratings. Eligible participants can look forward to potentially receiving free solar panel installations, contributing to energy savings and improved home heating.
Smart Export Guarantee (SEG)
The Smart Export Guarantee (SEG) is an ongoing scheme available to UK homes equipped with a Microgeneration Certification Scheme (MCS) certificate or an equivalent document, including an export meter and up to a 5MW capacity installation. Based on fuel prices as of January 2024, SEG payments generally result in annual energy cost savings exceeding £100 for households.
Zero per cent VAT
From April 2022 to March 2027, the Zero per cent VAT scheme offers a financial break to individuals in England, Scotland, and Wales purchasing and installing solar panels (and battery storage systems, if bought alongside the solar panels and installed by the same supplier). The savings under this incentive are contingent on the cost of the solar panels, reducing the overall expense of adopting renewable energy solutions.

Environmental Impact
Understanding the environmental impact of solar panels is crucial when considering them as a sustainable energy source. This guide to solar panels wouldn’t be complete without an in-depth look at this aspect.
First and foremost, solar panels significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Unlike fossil fuels, they generate electricity without releasing carbon dioxide or other harmful pollutants. This clean energy production plays a vital role in combating climate change. For context, a typical residential solar panel system can eliminate three to four tons of carbon emissions each year—the equivalent of planting over 100 trees annually.
Additionally, solar panels help in reducing water usage. Traditional electricity production can be water-intensive, especially in processes like cooling and refining. Solar energy, in contrast, requires minimal water to operate, making it a more sustainable choice in areas facing water scarcity.
However, it’s important to acknowledge that the manufacturing process of solar panels isn’t entirely without environmental impact. It involves the use of energy and resources, and the production of some waste. But, compared to the long-term impact of conventional energy sources, the footprint is significantly smaller.
Where Solar Panels Make a Difference
Decrease in Air Pollution:
By replacing fossil fuels, solar panels contribute to cleaner air. This improvement in air quality can have a direct positive impact on public health, reducing problems like asthma and bronchitis.
Reduction in Water Pollution:
Solar panels don’t pollute local water resources, or compete with agriculture, drinking systems, or other vital water needs.
Preservation of Habitats:
Solar farms provide an environmentally friendly option by utilizing degraded land for construction, minimizing habitat disruption. In contrast to other energy sources, such as coal or gas plants, solar farms offer a gentler approach to land use, ensuring coexistence with local wildlife through thoughtful planning.

In conclusion, this guide to solar panels shows that their environmental impact is overwhelmingly positive. While not entirely without footprint, solar panels are a giant leap forward in reducing our ecological impact and moving towards a more sustainable future.
Compatibility and Integration
When considering a solar power system, understanding its compatibility and integration is crucial. This guide to solar panels will delve into how solar panels integrate with existing systems and the compatibility factors you need to consider.
Integration with Existing Electrical Systems
Solar panels must seamlessly integrate with your existing electrical system. This involves connecting the solar panel array to your home’s electrical grid. An essential component in this process is the inverter, which converts the direct current (DC) electricity generated by the panels into alternating current (AC) electricity used in homes.

Compatibility with Roofing Materials
Your roof’s material plays a significant role in the installation and efficiency of solar panels. Most solar panels are compatible with various roofing materials like asphalt shingles, metal, or tiles. However, the installation method may differ. For instance, installing solar panels on a tile roof may require additional framing to distribute weight evenly.
Smart Home Integration
In our digital era, the synergy between solar panels and smart home technology is pivotal for effective energy management. Beyond simple monitoring, especially for grid-tied systems, load management through switching between various inputs is essential. Additionally, systems with battery integration or both grid and battery connections necessitate sophisticated software for optimal operation. This integration empowers users to track energy production and consumption in real-time via smartphone apps, maximizing efficiency and promptly identifying any performance issues.
Battery Storage Compatibility
Battery storage is a smart choice for anyone seeking to optimise their solar energy usage. By storing excess solar energy, batteries ensure uninterrupted power supply even on cloudy days. Moreover, leveraging cheaper night-time tariffs to charge up the battery offers attractive economic benefits. Compatibility between your solar panels and the battery system, including voltage and capacity, is crucial for seamless integration and optimal performance.
Grid Connectivity
For homes connected to the power grid, understanding grid interactivity is vital. This guide to solar panels emphasises that a grid-tied system allows you to feed excess electricity back into the grid, often earning credits on your electricity bill. However, compatibility with grid requirements, including specific inverter specifications, is essential for smooth operation.
In conclusion, ensuring compatibility and seamless integration of your solar panel system with existing structures and technologies is key to maximising benefits. As you explore the world of solar energy, keep these factors in mind for an efficient, productive solar power experience.

Location and Climate Considerations
When diving into the world of solar energy, understanding the influence of location and climate is crucial. This section of our comprehensive guide to solar panels focuses on how these factors affect solar panel performance and efficiency.
Location Matters
Firstly, your geographical location plays a significant role in the effectiveness of solar panels. Areas closer to the equator typically receive more direct sunlight year-round, making them ideal for solar installations. However, this doesn’t mean that solar panels are ineffective in northern or southern latitudes. For example, even in Northern Scotland, with its higher latitude compared to regions in Southern England, have successfully harnessed solar energy thanks to technological advancements and proper panel positioning.

Climate Impact
Solar panels play a crucial role in combating climate change by reducing reliance on fossil fuels for electricity generation. By harnessing energy from the sun, solar panels produce clean, renewable electricity without emitting harmful greenhouse gases. This shift towards solar energy helps to mitigate the environmental impacts associated with traditional energy sources, such as coal and natural gas, which release carbon dioxide and other pollutants into the atmosphere when burned for power generation.
Additionally, widespread adoption of solar panels contributes to a decrease in overall carbon emissions, helping to curb global warming and its associated effects, including rising temperatures, sea level rise, and extreme weather events. As more households, businesses, and communities embrace solar technology, the collective impact of reducing carbon emissions becomes increasingly significant, paving the way towards a more sustainable and climate-resilient future.
Temperature Considerations
Temperature is another critical aspect. Contrary to what you might think, solar panels can lose efficiency in extremely hot conditions. They operate best in cooler temperatures, which is why a cloudy cool day can be more productive for solar energy than a cloudy hot one.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while location and climate are influential in the world of solar panels, advancements in technology have made it possible for solar energy to be a viable option in a variety of settings. When considering solar panels, it’s essential to evaluate your specific location and climate, but don’t be deterred if you’re not in the sunniest spot on the map. With the right setup, solar energy can be harnessed effectively in many environments.
As we continue our guide to solar panels, remember: every location has its unique solar potential. Identifying and optimising for your specific conditions is key to successful solar energy use.
Common Myths and Misconceptions
Solar energy, despite its growing popularity, is often shrouded in myths and misconceptions. This section of our guide to solar panels aims to debunk these fallacies, helping you make an informed decision.
Myth 1: Solar Panels Don’t Work on Cloudy Days
Contrary to popular belief, solar panels do function on cloudy days. While it’s true that efficiency decreases, they still generate power. In fact, regions known for their overcast weather can still manage to be global leaders in solar energy – take Germany for example!

Myth 2: Solar Energy is Too Expensive
Initially, the cost of solar panels can be intimidating. However, considering long-term savings on electricity bills and available government incentives, solar energy is increasingly affordable. This guide to solar panels has earlier detailed the cost analysis, showing the potential savings.
Myth 3: Solar Panels Require Constant Maintenance
Actually, solar panels require minimal maintenance. They need an occasional cleaning to remove dust or debris and a regular check-up, typically once a year. This is far less upkeep than many other home systems.
Myth 4: Solar Panels Will Damage Your Roof
This is a common concern. However, when installed professionally, solar panels can protect and preserve the part of the roof they cover. Importantly, ensure your roof is in good condition before installation.
Myth 5: Solar Panels are Bad for the Environment
While solar panel production does have an environmental footprint, their long-term operation is far more eco-friendly compared to traditional energy sources. The reduction in carbon emissions and reliance on renewable energy sources significantly outweighs the initial production impact.

Myth 6: Solar Panels Will Lower Your Property Value
On the contrary, solar panels can increase property value. Homes with solar panels often sell faster and at higher prices than those without.
In conclusion, understanding and dispelling these myths is crucial in evaluating the feasibility and benefits of solar panels. With this knowledge, our guide to solar panels hopes to steer you towards a more sustainable and economically sound future.
Myth 7: Solar Panels are Unsightly
A common misconception about solar panels is that they are unsightly and detract from the aesthetic appeal of a property. However, modern solar panel systems have evolved to address this concern. Roof-mounted systems can now be installed flush with existing tiles, blending seamlessly with the roofline and maintaining the visual integrity of the property. Additionally, ground-mounted arrays, often referred to as solar gardens, offer an alternative option for homeowners concerned about rooftop aesthetics. These arrays can be strategically positioned in gardens or open spaces, minimizing their impact on the visual landscape while still harnessing the power of the sun for renewable energy generation.
Conclusion and Recommendations
In wrapping up our comprehensive guide to solar panels, it’s crucial to revisit the key takeaways and provide practical recommendations for those considering solar energy. This journey through the solar panel landscape illuminates a path toward a more sustainable and cost-effective future.
Embracing Solar Energy: A Wise Decision
First and foremost, adopting solar technology is a wise decision for most households. The initial investment, though significant, pays dividends in the long run through reduced energy bills and increased property value. Furthermore, as discussed in the “Cost Analysis” section, solar panels are becoming increasingly affordable.

Local Factors Matter
When considering solar panel effectiveness, factors like roof size, shape, and shade from nearby trees or buildings are crucial. While location plays a role, modern panels are remarkably efficient even in less sunny regions. So, regardless of where you live, solar energy remains a viable option for many households.
Maintenance and Longevity: Less Worrisome Than Perceived
Maintenance, a common concern addressed in “Maintenance and Durability,” is less daunting than it seems. Solar panels require minimal upkeep and are built to withstand harsh weather conditions, ensuring longevity and performance.
Utilising Incentives
Don’t overlook government incentives. As detailed in “Government Incentives and Subsidies,” these can significantly offset your initial costs. Stay informed about local subsidies and tax credits to make the most of your investment.
Debunking Myths: An Informed Choice Is Crucial
Finally, let’s not forget the importance of dispelling myths. As we’ve seen in “Common Myths and Misconceptions,” misinformation can deter potential solar panel users. Equip yourself with factual information to make an informed decision.

By embracing solar energy, you’re not just investing in your home – you’re contributing to a greener, more sustainable future. Thank you for following this guide to solar panels, and may your journey toward solar energy be enlightening and fruitful!
For more content you might find interesting, check out our 12 Solar Panel Mistakes to Avoid, or our guide to Best Solar Portable Power Stations.