Table of contents
Introduction to global solar power trends
The shift toward renewable energy is more urgent than ever as the world seeks sustainable solutions to a growing energy crisis and the escalating impacts of climate change. Among renewable resources, solar power has emerged as a key player due to its vast potential and increasing cost-effectiveness.
In recent years, the expansion of global solar capacity has been remarkable. According to a 2021 report by the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), solar photovoltaic (PV) generation saw an increase of 179 terawatt-hours – a 22% rise from the previous year, bringing global solar capacity to an impressive 849 gigawatts (GW). As of 2021, solar energy contributed approximately 3.6% to the world’s electricity generation, underscoring its growing role in the global energy mix.
Countries around the world are ramping up their solar energy capacities, driven by the dual needs of reducing carbon emissions and securing energy independence. This trend is supported by technological advancements, reducing costs, and supportive government policies, which have collectively enhanced the economic viability of solar power.
Five countries stand out for their contributions to global solar capacity. These nations not only lead in terms of installed capacity but also exemplify the diverse strategies and policies that can help other countries harness the sun’s power more effectively. By looking these leaders, we can learn valuable lessons about integrating solar energy into national grids and the crucial role of policy support in facilitating this transition.
Top 5 countries in solar energy
| Rank | Country | Solar capacity (GW) | Key details |
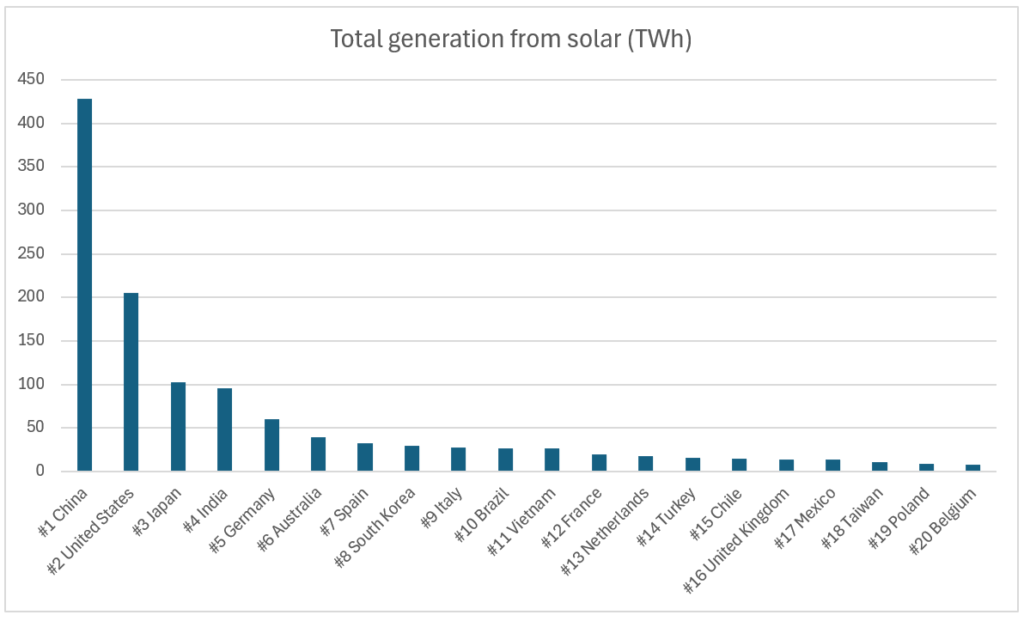
| #1 | China | 430 | World's largest producer and manufacturer of solar equipment. Accounts for approx. 50% of global solar capacity. |
| #2 | USA | 141.8 | Rapid growth in solar jobs; aims for 100% clean energy by 2025. |
| #3 | Japan | 84.9 | Increased capacity from 0.3% in 2010 to 10% of electricity in 2021. |
| #4 | Germany | 69.1 | Leading Europe's renewable transition; targeting 215 GW by 2030. |
| #5 | India | 68 | Targets 280 GW by 2030; strong governmental support and initiatives. |
2022 global rankings
All facts and figures in this article are derived from industry reports, reputable databases, and secondary data analysis articles, including statistics from the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) and Statista, along with global investment figures from Bloomberg NEF.
Solar capacity refers to the maximum amount of electrical power that a country, or a specific solar installation, can produce under optimal conditions. It is measured in gigawatts (GW) and indicates the total installed capability to generate electricity from solar panels at any given time. This figure helps quantify a nation’s solar energy potential based on the cumulative output capacity of all installed solar systems.
#1. China
China stands at the forefront of the global solar energy landscape, not only as the largest producer of solar power but also as the dominant force in solar technology manufacturing. With an astounding solar capacity of 430 gigawatts (GW) as of April 2023, China’s strategic investments and government policies have significantly shaped its leading position in the solar industry.

China’s rapid expansion and government support
China’s journey to becoming a solar superpower has been marked by rapid expansion and robust government support. In the first half of 2022 alone, the nation deployed over 30.88 GW of solar PV systems, with plans to install a total of 108 GW within the year. This development is supported by substantial financial investment, with China having invested over $50 billion in new PV supply capacity since 2011 – a figure ten times greater than that invested by Europe in the same timeframe.
Manufacturing and global market dominance
China’s dominance extends beyond its borders, controlling more than 80% of all manufacturing phases of solar panels. This control over the supply chain not only secures China’s position in the global market but also drives down costs worldwide, making solar power more accessible and affordable. The country’s approach has enabled the production of subsidy-free solar power that is cheaper than coal, providing a competitive edge in both domestic and international markets.
Future goals and international impact
Looking forward, China continues to set ambitious targets for its renewable energy sector. Under its 14th Five-Year Plan, China aims for 33% of its electricity to be generated from renewable sources by 2025. Moreover, President Xi Jinping has announced plans to develop 1200 GW of solar and wind energy capacity by 2030, reinforcing China’s commitment to leading the global shift towards renewable energy.
#2. United States
The United States is currently the second-largest producer of solar energy, with a capacity of 141.8 gigawatts (GW). Their growth is being fuelled by both innovative technology and supportive policies that aim to expand solar capacity across the nation.

Growth and technological advancements
From a modest 0.34 GW in 2008, the solar capacity in the U.S. has grown exponentially due to continuous technological advancements and decreasing costs of solar installations. American companies are at the forefront of developing high-efficiency solar panels and integrating solar technology into diverse applications, from residential rooftops to large-scale utility farms. This technological edge is supported by a strong foundation of research from institutions like the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), which continues to push the boundaries of solar efficiency and integration.
Policy support and market expansion
The U.S. government has played a pivotal role in the solar sector’s expansion through various incentives and policies. The policy move under President Joe Biden’s administration aims for 100% clean energy by 2025, with solar expected to meet 40% of this demand. This target is backed by policies such as federal tax credits and grants, which have substantially lowered the barrier to solar adoption both for utilities and individual consumers.
Solar's role in the national energy mix
Currently, solar power accounts for about 3% of the United States’ electricity, but this figure is expected to grow rapidly as more states adopt renewable energy mandates and as solar becomes increasingly cost-competitive. The potential for solar in the U.S. is vast – according to NREL, covering an area the size of Lake Michigan with solar panels could power the entire country if efficiency improvements continue.
Future outlook
The future of solar power in the United States looks bright, with ongoing advancements in solar technology and strong governmental support driving the market forward. The commitment to expanding solar capacity is not only a response to the increasing demand for electricity but also a strategic move to ensure energy independence and reduce carbon emissions. As solar technology becomes more integrated into America’s energy landscape, it sets a precedent for how renewable resources can effectively replace traditional energy sources and lead the transition towards a sustainable future.
#3. Japan
Japan is a leader in the efficient use of solar energy, currently standing as the third largest in solar power capacity worldwide. With a particular focus on technology and grid integration, Japan has successfully incorporated solar power to meet a significant portion of its energy needs.

Strategic growth and technological leadership
As of 2024, Japan’s capacity stands at 84.9 gigawatts (GW). This growth is supported by Japan’s technological leadership in photovoltaic (PV) cell production, where it has historically been a pioneer. The country’s manufacturers are known for their high-quality, efficient solar products, which have propelled both domestic and global solar markets.
Integration into the national grid
Solar power now accounts for close to 10% of Japan’s total electricity production, a significant increase from just 0.3% in 2010. This is in part due to Japan’s successful efforts in integrating solar power effectively into its national grid. Such integration has been facilitated by advanced technology that maximizes the efficiency of solar panels, even in areas with less sunlight compared to other leading solar nations.
Government policies and future targets
The Japanese government has played a crucial role in this expansion through incentives and supportive policies. Looking forward, Japan plans to add 20 GW of solar capacity in the next eight years, aiming to reach a target of 108 GW. This goal is part of a broader strategy to increase renewable energy use in response to past challenges, including the reduction of nuclear energy reliance following the Fukushima incident.
Adaptation and local initiatives
Japan’s approach also includes adapting solar solutions to its unique geographic and urban landscape. The government has initiated plans to install solar panels on over 50% of central government and municipal buildings.
#4. Germany
Germany is a leader in renewable energy within Europe, particularly when it comes to solar power. With a robust infrastructure and forward-thinking policies, Germany is a perfect example of how policy can drive technological adoption and create a sustainable energy environment.

Rapid expansion and policy influence
Germany’s solar capacity reached 69.1 gigawatts (GW) in 2021, making it one of the largest solar producers in Europe. Solar power now accounts for about 10% of the nation’s total electricity consumption, a significant contribution reflecting years of concerted effort in renewable energy policy and investment. The German government has been instrumental in this expansion through incentives such as the EEG (Renewable Energy Sources Act), which initially provided feed-in tariffs to encourage the adoption of solar technology.
Responding to energy crises
The geopolitical landscape, particularly tensions and energy crises stemming from conflicts such as the war in Ukraine, has prompted Germany to intensify its focus on expanding renewable energy capacity. The recent push includes a tender to develop an additional 1.5 GW of solar energy to help mitigate the effects of reduced gas supplies. This strategy not only addresses immediate energy security concerns, but also aligns with Germany’s long-term goals for sustainability.
Long-term goals and innovations
Looking towards the future, Germany aims to achieve net neutrality by 2045, with intermediate targets set for 2030. The country aims to install up to 215 GW of solar capacity by 2030, a significant step towards their overall energy transition goals. The government supports these targets with a variety of initiatives, including subsidies for solar installations and innovative projects like “Agri-PV” (agricultural photovoltaics), which combines agriculture with solar energy production.
Cultural acceptance and public support
Public support and cultural acceptance of solar energy have also played a significant role in the widespread adoption across Germany. The German population has shown a strong preference for sustainable practices, which has been reflected in consumer behaviours and local government policies that favour green technology.
#5. India
At number five, India is a fast-growing and high-potential player in the global solar power landscape. With a focus on both enhancing capacity and technological innovation, India is rapidly increasing its solar capabilities.

Impressive growth in solar capacity
India’s recent journey in solar energy expansion is impressive, having reached an installed capacity of over 68 gigawatts (GW) by 2023. This achievement places India among the top five global leaders in solar energy, sitting just behind Germany. The country has capitalized on its geographical advantage, receiving abundant sunshine for more than 300 days a year, making it an ideal candidate for solar power generation.
Government initiatives and policies
The Indian government has been key in accelerating the adoption of solar energy through aggressive policy frameworks and substantial investments. Key initiatives include the Performance Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for high-efficiency solar PV panels, which encourages the domestic production of solar equipment. This policy not only aims to meet internal demand, but also to reduce the dependency on imports, increasing India’s position in the global solar market.
In the first half of 2022 alone, India added 7.2 GW of solar capacity, with plans to reach a ginormous 280 GW by 2030.
Challenges and opportunities
Despite its rapid progress, India faces challenges such as land acquisition issues, financial constraints, and the need for technological advancements in solar storage solutions. However, the government continues to address these hurdles through innovative policies and by encouraging private and international investments.
Future prospects
India’s future in solar energy looks promising, with the government actively promoting solar through various subsidies and incentives. The focus on building a robust manufacturing ecosystem for solar components aligns with India’s ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat‘ (“self-reliant India”) initiative, aiming to make the country a global hub for solar technology.
Conclusion: Lessons learned and the path forward
The experiences of China, the United States, Japan, Germany, and India in developing their solar energy sectors provide valuable insights into the diverse strategies that can effectively boost solar power adoption. Each country’s approach highlights the importance of tailored policies, robust government support, technological innovation, and public acceptance.
Policy and government support
Strong policy frameworks are crucial, as seen in all five countries. These policies, whether in the form of incentives like tax rebates and feed-in tariffs or ambitious renewable energy targets, significantly impact the growth of solar capacity. Supportive regulations not only encourage local developments but also attract international investment.
Technological advancements
Technological innovation is key to overcoming the efficiency and storage challenges associated with solar power. Japan and Germany, for example, demonstrate how continuous technological advancement can lead to higher efficiency and better integration of solar systems into existing power grids.
Adapting to local conditions
Understanding and adapting to local conditions is essential for maximizing the potential of solar energy. India’s focus on building domestic manufacturing capabilities and the U.S.’s emphasis on diversifying solar applications across various states are indicative of strategies that consider local resources and needs.
The future of global solar power
The progress made by these leading countries provides a roadmap that others can adapt and refine according to their specific circumstances and capacities.
Looking forward, the path for solar energy seems focused on enhancing grid integration and storage solutions to manage intermittency and ensure a stable energy supply. It’s certain that expanding the role of solar power in global energy markets will require ongoing innovation, increased economic incentives, and international cooperation.
For further reading, you might enjoy the following:





